
Bladder and urinary tract infections can be embarrassing. The constant feeling of having to run to the bathroom, the burning and discomfort. It’s not fun. But over 50% of all women will have to deal with a bladder infection at least once in their life.
It’s a perfectly natural occurrence that we, unfortunately, sometimes must suffer through. By knowing the signs and causes, you can make sure you get treatment early or (even better) avoid infection altogether!
Men, with their longer urethras, are less at risk. But you guys aren’t completely in the clear, so this is for you as well!
What is a Bladder Infection?
A bladder infection, or cystitis, seems rather straightforward: a bacterial infection of the bladder. However, they aren’t always that easy.
Bladder infections come in two varieties: simple or complicated. Simple bladder infections are commonly caused by E. coli and are easy to treat with antibiotics. Complicated bladder infections (as the name implies) are more difficult.
While simple bladder infections occur in healthy individuals, complicated bladder infections may be caused by other factors. Pregnancy, diabetes, catheters, and urinary stents can all contribute to complicated bladder infections.
No matter the cause, bladder infections are unpleasant, uncomfortable, and shouldn’t be ignored.
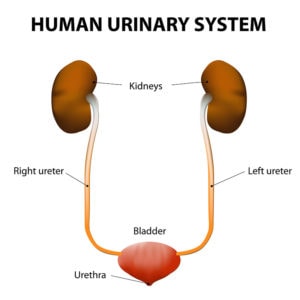 Bladder Infection vs UTI
Bladder Infection vs UTI
A bladder infection is quite different from a UTI. A UTI refers to the entire urinary system, including the bladder, ureters (the tube connecting the kidneys to the bladder), urethra (opening to the urinary tract), and kidneys. However, a bladder infection (as the name implies) is just an infection of the bladder.
A bladder infection is a type of UTI, but not all UTIs will affect the bladder.
What are the symptoms of a bladder infection?
Common symptoms of a simple bladder infection include:
-
- Pain when urinating
- Increased frequency of urination
- Sudden urge or need to urinate
- Pain in the lower abdomen
- Incontinence (loss of bladder control)
Complicated bladder infections include the same symptoms as above, plus:
-
- Nausea and vomiting
- Headache
- Fever
What causes bladder infections?
In simple terms: bacteria.
The body usually flushes out microorganisms in the bladder through urination. However, bacteria can attach themselves to the walls of the bladder and multiply, resulting in a bladder infection.
The bacteria that usually cause bladder infections come from the bowels. Women are more prone to bladder infection because they have shorter urethras allowing an easier path for bacteria to get to the bladder.
Women have a higher risk of bladder infections due to:
-
- Sexual activity
- Birth control methods such as diaphragms or spermicidal agents
- Menopause
- Pregnancy
Bladder Infection in Men
For men, the primary risk factor for bladder infections is an enlarged prostate. A larger prostate obstructs urine flow, increasing the risk of infection. Bladder infections are much less common in men, especially before the age of 50, and usually indicate an underlying urologic abnormality, such as kidney stones or other obstructions of the urinary tract.
Seeing a urologist may be recommended.
How do you diagnose bladder infections?
If you suspect you have a bladder infection, you should get a confirmed diagnosis from your healthcare provider. This will ensure you get proper treatment for the infection. A urine culture analysis will also confirm whether the infection has spread to the kidneys.
Your doctor will discuss your symptoms with you and may do urine tests or urinalysis to confirm the diagnosis. The presence of antibodies and white blood cells in urine samples indicates a bladder infection.
Bladder Infection Treatments
The most common treatment option for a bladder infection, especially a simple one, is antibiotics. Based on your symptoms and severity, your medical treatment might include trimethoprim, nitrofurantoin, ceftriaxone, or cephalexin. While your symptoms may begin to improve after starting treatment, complete the full medication regimen to prevent recurrence of the infection.
On the other hand, if symptoms haven’t improved after two or three days of treatment, follow up with your doctor.
Complicated bladder infections don’t respond well to direct treatment. Underlying conditions make complicated bladder infections worse and harder to treat.
Factors that make a bladder infection complicated:
Recurrent infections
If you have repeated bladder infections, you may need a different treatment plan. Treatment may include a longer course of antibiotics or daily antibiotics by IV.
Kidney Damage
An untreated bladder infection can spread to surrounding organs and tissues, including the kidneys. A kidney infection (pyelonephritis) can cause long-term damage, including kidney scarring and high blood pressure.
Diabetes
Because diabetes negatively impacts the immune system, it can worsen the symptoms of bladder infections.
Pregnancy
Because your bladder is compressed, you have an increased risk of bladder infections while pregnant. If left untreated, the infection can cause complications not only for you but the baby as well.
Are there bladder infection home remedies?
Absolutely! As they say, the best offense is a good defense. Instead of treating a bladder infection, try to prevent one altogether! Some recommended prevention strategies include:
 Change Birth Control
Change Birth Control
As previously mentioned, spermicides and diaphragms can increase your risk of a bladder infection.
Drink Lots of Water
When you’re well hydrated, you urinate more often. More frequent urination helps flush out bacteria.
Urinate After Sex
Sexual intercourse can expose a woman’s urethra to bacteria that then travels into the bladder and causes an infection. Urinating helps flush out bacteria that may enter the urethra.
Washing Frequently
Keeping the genital area clean decreases the risk of bacteria making its way up the urethra.
Cranberry Juice and Supplements
Cranberry juice has been used for generations as a natural treatment against bladder infections. A 2012 review demonstrated that cranberry shows promise a remedy for those who frequently suffer bladder infections. If you’re taking cranberry juice or tablets, be sure to tell your doctor as it may impact the effectiveness of some antibiotics.
About Dr. Thaïs Aliabadi
As one of the nation’s leading obstetricians, Dr. Thaïs Aliabadi offers the very best in gynecology and obstetrics care. Together with her warm professional team, Dr. Aliabadi supports women through all phases of life. She fosters a special one-on-one relationship between patient and doctor.
We take our patients’ safety very seriously. Our facility’s Covid-19 patient safety procedures exceed all CDC recommendations. Masks are required in our office at all times.
We invite you to establish care with Dr. Aliabadi. For appointment requests or general inquiries, click here or call us at (844) 863-6700.
We take our patients’ safety seriously. Our office and surgery center’s Covid-19 patient safety procedures exceed all CDC recommendations. Masks are required in our institutes at all times.
The practice of Dr. Thais Aliabadi and the Outpatient Hysterectomy Center are conveniently located for patients throughout Southern California and the Los Angeles area. We are in Beverly Hills and near West Hollywood, Santa Monica, West Los Angeles, Culver City, Hollywood, Venice, Marina del Rey, Malibu, Manhattan Beach, and Downtown Los Angeles.

